Java Spring Application Errors Example Code
In this tutorial, we will learn how to handle exceptions for RESTful Web Services developed using Spring Boot.
We can handle exceptions in REST API in the same way we handle them in the SpringMVC based web application that is by using the @ExceptionHandler and @ControllerAdvice annotations. Instead of rendering a view, you can return ResponseEntity with the appropriate HTTP status code and exception details in JSON/XML format.
By default, Spring Boot provides a /error mapping that handles all errors in a sensible way, and it is registered as a "global" error page in the servlet container. Rest clients, it produces a JSON response with details of the error, the HTTP status, and the exception message.
Instead of simply throwing an exception with the HTTP status code, it is better to provide more details about the issue, such as the error code, message, cause, etc. In this example, we define a class annotated with@ControllerAdvice to customize the JSON document to return for a particular controller and/or exception type.
Spring Boot Exception Handling Workflow
We will implement exception handling in Spring boot as per the below workflow:

Tools and Technologies Used
- Spring Boot
- JDK - 1.8 or later
- Spring MVC
- Hibernate
- Maven
- Spring Data JPA
- IDE - Eclipse or Spring Tool Suite (STS) or Intellij IDEA// Any IDE works
- MYSQL
1. Create Spring boot application
Spring Boot provides a web tool called Spring Initializer to bootstrap an application quickly. Just go to https://start.spring.io/ and generate a new spring boot project.
Use the below details in the Spring boot creation:
Project Name: springboot-blog-rest-api
Project Type:Maven
Choose dependencies: Spring Web, Lombok, Spring Data JPA, Spring Security, Dev Tools, and MySQL Driver
Package name:net.javaguides.springboot
Packaging: Jar
Download the Spring Boot project as a zip file, unzip it and import it in your favorite IDE.
2. Maven Dependencies
Here is the pom.xml file for your reference:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.4.2</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>com.springboot.blog</groupId> <artifactId>springboot-blog-rest-api</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>springboot-blog-rest-api</name> <description>Spring boot blog application rest api's</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <excludes> <exclude> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </exclude> </excludes> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project> 3. Configure MySQL Database
Let's first create a database in MySQL server using the below command:
Since we're using MySQL as our database, we need to configure the database URL , username , and password so that Spring can establish a connection with the database on startup. Open src/main/resources/application.properties file and add the following properties to it:
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myblog?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC spring.datasource.username = root spring.datasource.password = root # hibernate properties spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect # Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, validate, update) spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update logging.level.org.springframework.security=DEBUG
4. Model Layer - Create JPA Entity
Let's create a Post JPA entity:
package com.springboot.blog.entity; import lombok.*; import javax.persistence.*; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; @Getter @Setter @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor @Entity @Table( name = "posts", uniqueConstraints = {@UniqueConstraint(columnNames = {"title"})} ) public class Post { @Id @GeneratedValue( strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY ) private Long id; @Column(name = "title", nullable = false) private String title; @Column(name = "description", nullable = false) private String description; @Column(name = "content", nullable = false) private String content; } 5. Repository Layer
Let's create a PostRepository to retrieve and save post records in the MySQL database:
package com.springboot.blog.repository; import com.springboot.blog.entity.Post; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; public interface PostRepository extends JpaRepository<Post, Long> { } 6. Exception(Error) Handling for RESTful Services
Spring Boot provides a good default implementation for exception handling for RESTful Services.
Let's quickly look at the default Exception Handling features provided by Spring Boot.
If we try to get a post by id from the database and the post is not exist in the database with the given id then Spring boot will return the default error response as below:
{ "timestamp": "2021-02-28T14:15:18.250+00:00", "status": 404, "error": "Not Found", "trace": "com.springboot.blog.exception.ResourceNotFoundEx ception: Post not found with id : '6'……... "message": "Post not found with id : '6'", "path": "/api/posts/6" } Default error response provided by Spring Boot contains all the details that are typically needed.
However, you might want to create a framework independent response structure for your organization. In that case, you can define a specific error response structure. For example:
{ "timestamp": "2021-02-28T14:13:47.572+00:00", "message": "Post not found with id : '6'", "details": "uri=/api/posts/6" } Let's write the code to customize the error response of the Spring boot REST API.
ErrorDetails
package com.springboot.blog.payload; import java.util.Date; public class ErrorDetails { private Date timestamp; private String message; private String details; public ErrorDetails(Date timestamp, String message, String details) { this.timestamp = timestamp; this.message = message; this.details = details; } public Date getTimestamp() { return timestamp; } public String getMessage() { return message; } public String getDetails() { return details; } } ResourceNotFoundException
Let's create a ResourceNotFoundException.java class and add the following content to it:
package com.springboot.blog.exception; import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus; @ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND) public class ResourceNotFoundException extends RuntimeException{ private String resourceName; private String fieldName; private long fieldValue; public ResourceNotFoundException(String resourceName, String fieldName, long fieldValue) { super(String.format("%s not found with %s : '%s'", resourceName, fieldName, fieldValue)); // Post not found with id : 1 this.resourceName = resourceName; this.fieldName = fieldName; this.fieldValue = fieldValue; } public String getResourceName() { return resourceName; } public String getFieldName() { return fieldName; } public long getFieldValue() { return fieldValue; } } Create GlobalExceptionHandler class
To use ErrorDetails to return the error response, let's create a GlobalExceptionHandler class annotated with @ControllerAdvice annotation. This class handles exception-specific and global exceptions in a single place.
package com.springboot.blog.exception; import com.springboot.blog.payload.ErrorDetails; import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler; import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest; import java.util.Date; @ControllerAdvice public class GlobalExceptionHandler { // handle specific exceptions @ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class) public ResponseEntity<ErrorDetails> handleResourceNotFoundException(ResourceNotFoundException exception, WebRequest webRequest){ ErrorDetails errorDetails = new ErrorDetails(new Date(), exception.getMessage(), webRequest.getDescription(false)); return new ResponseEntity<>(errorDetails, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND); } @ExceptionHandler(BlogAPIException.class) public ResponseEntity<ErrorDetails> handleBlogAPIException(BlogAPIException exception, WebRequest webRequest){ ErrorDetails errorDetails = new ErrorDetails(new Date(), exception.getMessage(), webRequest.getDescription(false)); return new ResponseEntity<>(errorDetails, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST); } // global exceptions @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) public ResponseEntity<ErrorDetails> handleGlobalException(Exception exception, WebRequest webRequest){ ErrorDetails errorDetails = new ErrorDetails(new Date(), exception.getMessage(), webRequest.getDescription(false)); return new ResponseEntity<>(errorDetails, HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR); } } 7. Service Layer
PostService
package com.springboot.blog.service; import com.springboot.blog.payload.PostDto; import com.springboot.blog.payload.PostResponse; import java.util.List; public interface PostService { PostDto createPost(PostDto postDto); PostResponse getAllPosts(int pageNo, int pageSize, String sortBy, String sortDir); PostDto getPostById(long id); PostDto updatePost(PostDto postDto, long id); void deletePostById(long id); } PostServiceImpl
package com.springboot.blog.service.impl; import com.springboot.blog.entity.Post; import com.springboot.blog.exception.ResourceNotFoundException; import com.springboot.blog.payload.PostDto; import com.springboot.blog.payload.PostResponse; import com.springboot.blog.repository.PostRepository; import com.springboot.blog.service.PostService; import org.springframework.data.domain.Page; import org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest; import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable; import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.List; import java.util.stream.Collectors; @Service public class PostServiceImpl implements PostService { private PostRepository postRepository; public PostServiceImpl(PostRepository postRepository) { this.postRepository = postRepository; } @Override public PostDto createPost(PostDto postDto) { // convert DTO to entity Post post = mapToEntity(postDto); Post newPost = postRepository.save(post); // convert entity to DTO PostDto postResponse = mapToDTO(newPost); return postResponse; } @Override public PostResponse getAllPosts(int pageNo, int pageSize, String sortBy, String sortDir) { Sort sort = sortDir.equalsIgnoreCase(Sort.Direction.ASC.name()) ? Sort.by(sortBy).ascending() : Sort.by(sortBy).descending(); // create Pageable instance Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(pageNo, pageSize, sort); Page<Post> posts = postRepository.findAll(pageable); // get content for page object List<Post> listOfPosts = posts.getContent(); List<PostDto> content= listOfPosts.stream().map(post -> mapToDTO(post)).collect(Collectors.toList()); PostResponse postResponse = new PostResponse(); postResponse.setContent(content); postResponse.setPageNo(posts.getNumber()); postResponse.setPageSize(posts.getSize()); postResponse.setTotalElements(posts.getTotalElements()); postResponse.setTotalPages(posts.getTotalPages()); postResponse.setLast(posts.isLast()); return postResponse; } @Override public PostDto getPostById(long id) { Post post = postRepository.findById(id).orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Post", "id", id)); return mapToDTO(post); } @Override public PostDto updatePost(PostDto postDto, long id) { // get post by id from the database Post post = postRepository.findById(id).orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Post", "id", id)); post.setTitle(postDto.getTitle()); post.setDescription(postDto.getDescription()); post.setContent(postDto.getContent()); Post updatedPost = postRepository.save(post); return mapToDTO(updatedPost); } @Override public void deletePostById(long id) { // get post by id from the database Post post = postRepository.findById(id).orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Post", "id", id)); postRepository.delete(post); } // convert Entity into DTO private PostDto mapToDTO(Post post){ PostDto postDto = new PostDto(); postDto.setId(post.getId()); postDto.setTitle(post.getTitle()); postDto.setDescription(post.getDescription()); postDto.setContent(post.getContent()); return postDto; } // convert DTO to entity private Post mapToEntity(PostDto postDto){ Post post = new Post(); post.setTitle(postDto.getTitle()); post.setDescription(postDto.getDescription()); post.setContent(postDto.getContent()); return post; } } 8. Controller Layer
package com.springboot.blog.controller; import com.springboot.blog.payload.PostDto; import com.springboot.blog.payload.PostResponse; import com.springboot.blog.service.PostService; import com.springboot.blog.utils.AppConstants; import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; import java.util.List; @RestController @RequestMapping("/api/posts") public class PostController { private PostService postService; public PostController(PostService postService) { this.postService = postService; } // create blog post rest api @PostMapping public ResponseEntity<PostDto> createPost(@RequestBody PostDto postDto){ return new ResponseEntity<>(postService.createPost(postDto), HttpStatus.CREATED); } // get all posts rest api @GetMapping public PostResponse getAllPosts( @RequestParam(value = "pageNo", defaultValue = AppConstants.DEFAULT_PAGE_NUMBER, required = false) int pageNo, @RequestParam(value = "pageSize", defaultValue = AppConstants.DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE, required = false) int pageSize, @RequestParam(value = "sortBy", defaultValue = AppConstants.DEFAULT_SORT_BY, required = false) String sortBy, @RequestParam(value = "sortDir", defaultValue = AppConstants.DEFAULT_SORT_DIRECTION, required = false) String sortDir ){ return postService.getAllPosts(pageNo, pageSize, sortBy, sortDir); } // get post by id @GetMapping("/{id}") public ResponseEntity<PostDto> getPostById(@PathVariable(name = "id") long id){ return ResponseEntity.ok(postService.getPostById(id)); } // update post by id rest api @PutMapping("/{id}") public ResponseEntity<PostDto> updatePost(@RequestBody PostDto postDto, @PathVariable(name = "id") long id){ PostDto postResponse = postService.updatePost(postDto, id); return new ResponseEntity<>(postResponse, HttpStatus.OK); } // delete post rest api @DeleteMapping("/{id}") public ResponseEntity<String> deletePost(@PathVariable(name = "id") long id){ postService.deletePostById(id); return new ResponseEntity<>("Post entity deleted successfully.", HttpStatus.OK); } } Create a classAppConstants and add the following code to it:
package com.springboot.blog.utils; public class AppConstants { public static final String DEFAULT_PAGE_NUMBER = "0"; public static final String DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE = "10"; public static final String DEFAULT_SORT_BY = "id"; public static final String DEFAULT_SORT_DIRECTION = "asc"; } 9. Demo
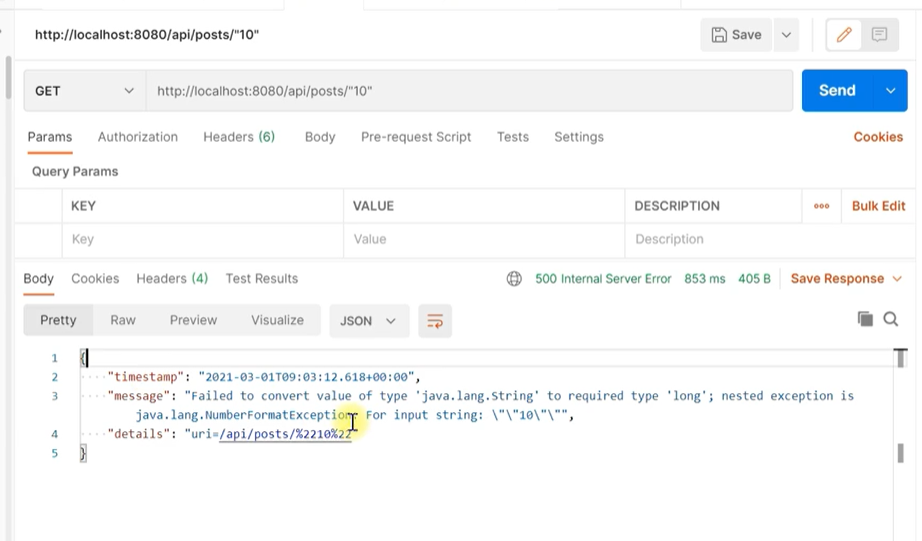
GitHub Repository
Video Course
References
Free Spring Boot Tutorial | Full In-depth Course | Learn Spring Boot in 10 Hours
Watch this course on YouTube at Spring Boot Tutorial | Fee 10 Hours Full Course
Source: https://www.javaguides.net/2021/10/spring-boot-exception-handling-example.html
0 Response to "Java Spring Application Errors Example Code"
Post a Comment